Introduction to the periodic table, elements, and atoms
LEARNING GOAL
By the end of this lesson, I will be able to:
SUCCESS CRITERIA
By the end of this lesson, I will be able to:
What is chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of matter. Matter is anything with a mass and a volume (takes up space). Matter is all around us. Your shirt, a book, the computer you are using, even the air you breathe is matter.
Matter is made up of tiny particles. Some of the most basic particles that make up matter are called atoms. Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that still retain the characteristics of that element. They cannot be broken down into smaller particles through mechanical means. Atoms are too small to be seen by the naked eye.
The three types of subatomic particles that make up atoms are protons, neutrons, and electrons. An element is made of many identical atoms. Think of an atom as a brick and an element as a large brick wall.
The gold coin is made up of millions of atoms of gold, and since all of the atoms in the gold coin are the same, it is an element. Therefore, millions of atoms of gold, which we cannot see with the naked eye, make up the element gold which we can see.
Protons, electrons, and neutrons
Powerful scanning tunnelling microscopes can only see atoms. However, inside the atom there are smaller particles called subatomic particles. Atoms form different elements because of the number and type of these subatomic particles. The majority of the mass of the atom comes from the proton and the neutron.
If the subatomic particles had weights of animals in the real world, the protons and neutrons would have the mass of a large dog and the electron would have the mass of a small mouse. That is the relationship between the mass of the protons, neutrons, and electrons.
The periodic table
The Periodic Table
In Chemistry, the Periodic Table can be used to determine many properties of different elements. We can use it to determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons each element has. Scientists created the Periodic Table so elements that share similar characteristics and traits are grouped together, just as members of a human family would be. There are 18 groups in the standard periodic table. A group (also known as a family) is a vertical column and a period is a row in the periodic table.
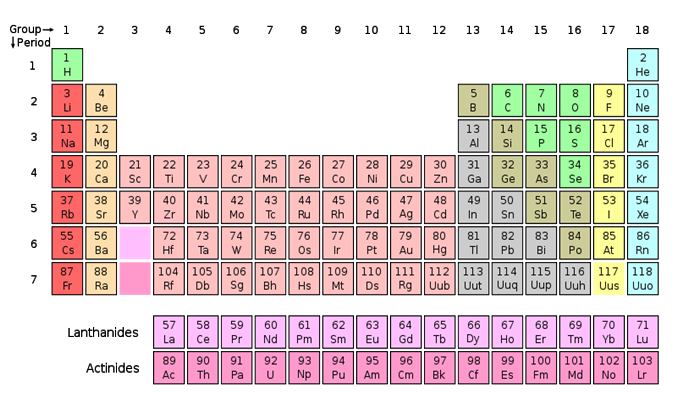 The different types, or flavours, of atoms are called elements. Each element is unique because its atoms have a specific number of subatomic particles. The number of protons found in all atoms of a given element is called that element's atomic number. The atomic number tells you how many protons and electrons the element has. The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom is called its atomic mass number. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
The different types, or flavours, of atoms are called elements. Each element is unique because its atoms have a specific number of subatomic particles. The number of protons found in all atoms of a given element is called that element's atomic number. The atomic number tells you how many protons and electrons the element has. The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom is called its atomic mass number. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams
A Bohr-Rutherford diagram can show the structure of any atom. In this type of diagram, the particles of the nucleus are shown in a circle and the electrons are shown in various orbitals surrounding the nucleus. The orbitals are always filled from the inside out, and can hold the following numbers of electrons:
1st orbital: can hold a maximum of 2 electrons
2nd orbital: can hold a maximum of 8 electrons
3rd orbital: can hold a maximum of 8 electrons
4th orbital: can hold a maximum of 2 electrons
These numbers are not exactly true, but are simplified for our purposes of drawing diagrams for elements with atomic numbers 1-20.
Ions and Bohr-Rutherford Diagrams
If an atom has a different number of protons than electrons, it is known as an ion. If the ion has more electrons than protons, it has an overall negative charge and is called an anion. If the ion has fewer electrons than protons, it has an overall positive charge and is called a cation.
 The different types, or flavours, of atoms are called elements. Each element is unique because its atoms have a specific number of subatomic particles. The number of protons found in all atoms of a given element is called that element's atomic number. The atomic number tells you how many protons and electrons the element has. The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom is called its atomic mass number. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.
The different types, or flavours, of atoms are called elements. Each element is unique because its atoms have a specific number of subatomic particles. The number of protons found in all atoms of a given element is called that element's atomic number. The atomic number tells you how many protons and electrons the element has. The number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom is called its atomic mass number. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes.